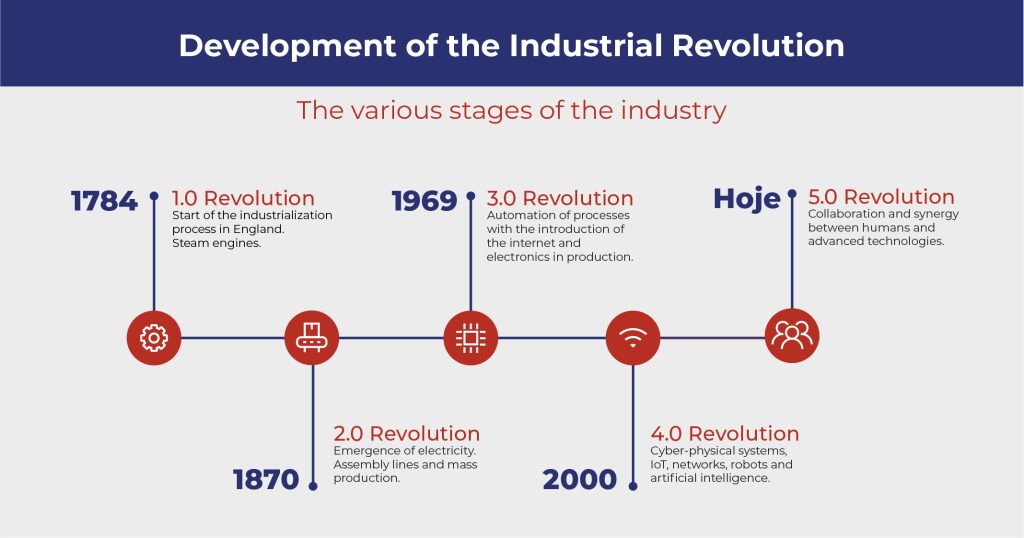
Over the years we have seen the evolution of industry, where major transformations have taken place, both economically and socially. The 1st Industrial Revolution began at the end of the 18th century in England. Since then, industry has gone through different phases, each marked by a significant advance in the way goods are produced and how societies have been structured, building the path to the modern world we know today.
Transition from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0
Only recently there was talk about how many companies were adapting to Industry 4.0, but a new industrial revolution is already underway, Industry 5.0.
The transition from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0 represents an evolution in the way products are manufactured, offering greater flexibility, sustainability and customisation.
Industry 4.0 is characterized by the automation, digitalisation and interconnection of industrial processes through advanced technologies (Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI)), while Industry 5.0 seeks to extend these concepts to create a more human and well-being-centred industrial environment.
Definition and origin of Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 refers to a new phase of industrial development that centres on collaboration between humans and intelligent machines, according to the European Commission.
This concept was launched in 2016 in Japan, having been developed by the Japan Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI) and the Japan Business Federation (Keidanren).
Some of the main characteristics that define Industry 5.0:
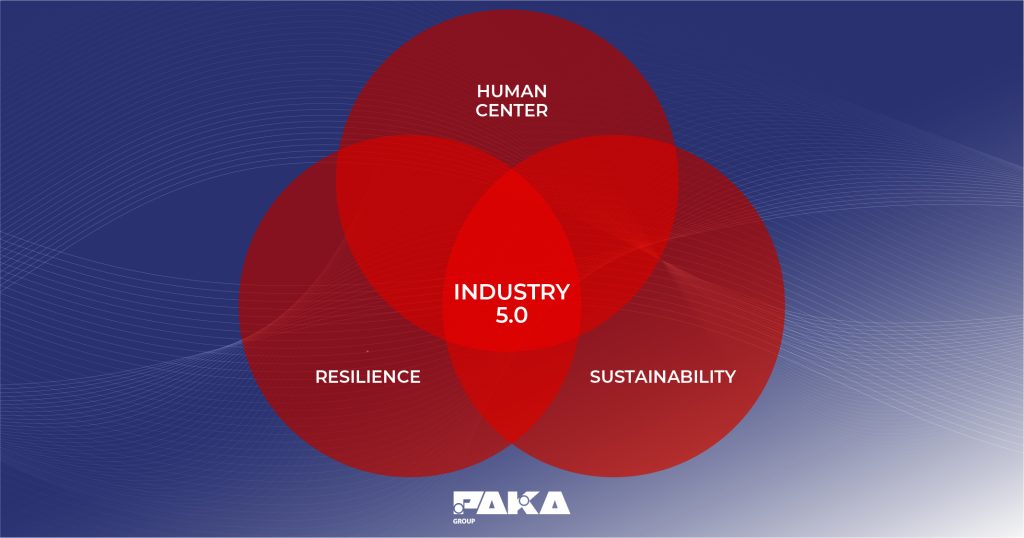
1. Human-machine collaboration
Industry 5.0 centres on collaboration between humans and robots. This involves the use of collaborative robots (cobots), which work side by side with humans. This collaboration aims not only to increase efficiency, but also to create safe working environments, promoting worker well-being. It also values human skills such as creativity, which are difficult for machines to portray.
2. Customization
Industry 5.0 enables large-scale personalized production. By combining the flexibility of digital production with human labour, companies can offer products that perfectly match consumers’ individual preferences, without compromising on efficiency and cost.
3. Sustainability
Industry 5.0 considers sustainability to be one of the key aspects for business success. This new industrial phase encourages greener production practices, efficient use of resources and a reduction in waste. Sustainability is seen not only as an ethical obligation, but also as a competitive advantage.
4. Resilience and Flexibility
Industry 5.0 prepares companies to be more resilient in the face of crises and market changes. This is achieved through flexible systems that can be quickly adapted to new conditions and needs. The ability to respond quickly is essential to face challenges such as pandemics, climate change and economic fluctuations.
Are companies ready for Industry 5.0?
Despite the advances, many companies are still in the implementation phase of Industry 4.0 technologies and may not be fully prepared for the demands of Industry 5.0.
Preparing a company for Industry 5.0 involves a series of technological, cultural and organisational adaptations. This new trend presents a new vision of industry that goes beyond the use of new technologies. It promotes interaction between human beings and intelligent technologies, making both complete and capable of working together.

Some fundamental steps to ensure that a company is prepared:
1. Assessment of current capabilities
Technological analysis: Assess the level of automation and integration of technologies in the company. Identify gaps in relation to the capabilities required by Industry 5.0, such as AI, IoT and cobots.
Skills analysis: Assess the current skills of workers and identify training or hiring needs to fill gaps, especially in areas such as emerging technologies.
2. Culture and change management
Culture of innovation: Foster an organisational culture that values innovation, experimentation and adaptability.
Employee involvement: Encourage employees to actively participate in the process of planning and implementing initiatives. This can include training programmes, workshops and open communication channels.
3. Integration of advanced technologies
Implementing AI and collaborative robotics: Investing in technologies that enable collaboration between humans and machines, such as cobots and Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems that can learn and adapt in real time.
Infraestruturas de Dados e IoT: Criar infraestruturas de recolha e análise de dados, incluindo sensores IoT e plataformas de Big Data. Isso permite melhores decisões e personalização de produtos.
4. Sustainability and social responsibility
Sustainable practices: Integrating sustainability into the company’s operations, from the use of environmentally friendly materials, optimising energy consumption and reducing waste.
Social responsibility: Ensuring that the implementation of Industry 5.0 is aligned with the principles of social responsibility, taking into account the social and ethical impacts of the new working model.
5. Partnerships and collaborations
Open innovation: Collaborate with start-ups, universities and research centres to explore new technologies and solutions. This can speed up innovation and reduce the time it takes to develop new products and processes.
Partner network: Build and maintain a network of partners who can provide support and expertise in specific areas such as AI, robotics and IoT.
There are already some companies at the forefront of this new industrial phase.
These examples show how Industry 5.0 is transforming various sectors by integrating advanced technologies with human collaboration.
Examples of companies and sectors
Automotive: Companies such as Tesla and BMW have been pioneers in the use of collaborative robotics for vehicle assembly, the use of AI to predict and improve vehicle maintenance, as well as sustainable production practices.
Food and Drink: Nestlé and Unilever are using automation and IoT to monitor and optimise production, as well as personalising products based on consumer preferences.
Health and Biotechnology: Companies like Johnson Johnson are exploring AI and robotics to develop personalized medical products.
Electronics and Technology: Apple and Samsung are investing in smart factories that use AI and IoT to improve production.
Industry 5.0 represents a more humanised approach to production, where advanced technologies are aligned with sustainability, resilience and human well-being.
Preparing for Industry 5.0 is an ongoing process that requires strategic investments, a change in mindset and constant adaptation to new technologies and trends. Companies that prepare for this transition will be better placed to seize the opportunities of this new industrial era. Industry 5.0 promises to transform the relationship between humans and machines, harnessing the best of both to create a more efficient, sustainable and human-centred production environment.